A Resource for Information on the Commonwealth's Geology
Featured Image
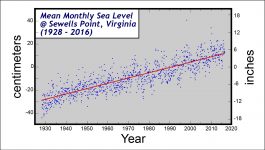
Sea Level Change at Sewells Point
The level of the sea has been measured at Sewells Point, Virginia continuously since 1928. In 1928 the mean level of the sea was ~45 cm ( ~18″) lower than it is in 2016. Sea level rise and regional land subsidence is creating an ever-growing problem in Hampton Roads and most of coastal Virginia.
What’s New in Virginia Geology
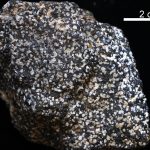
Virginia’s State Rock: Nelsonite
On July 1, 2016, Governor Terry McCauliffe signed a bill into law that made nelsonite the first official state rock of Virginia. The initiative for this project was led by students from Piedmont Virginia Community College. Michelle Stanislaus and her classmates from their Historical Geology class and Government class ran the petition for this law starting […]
Copyright © 2026 · Backcountry Child Theme on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in